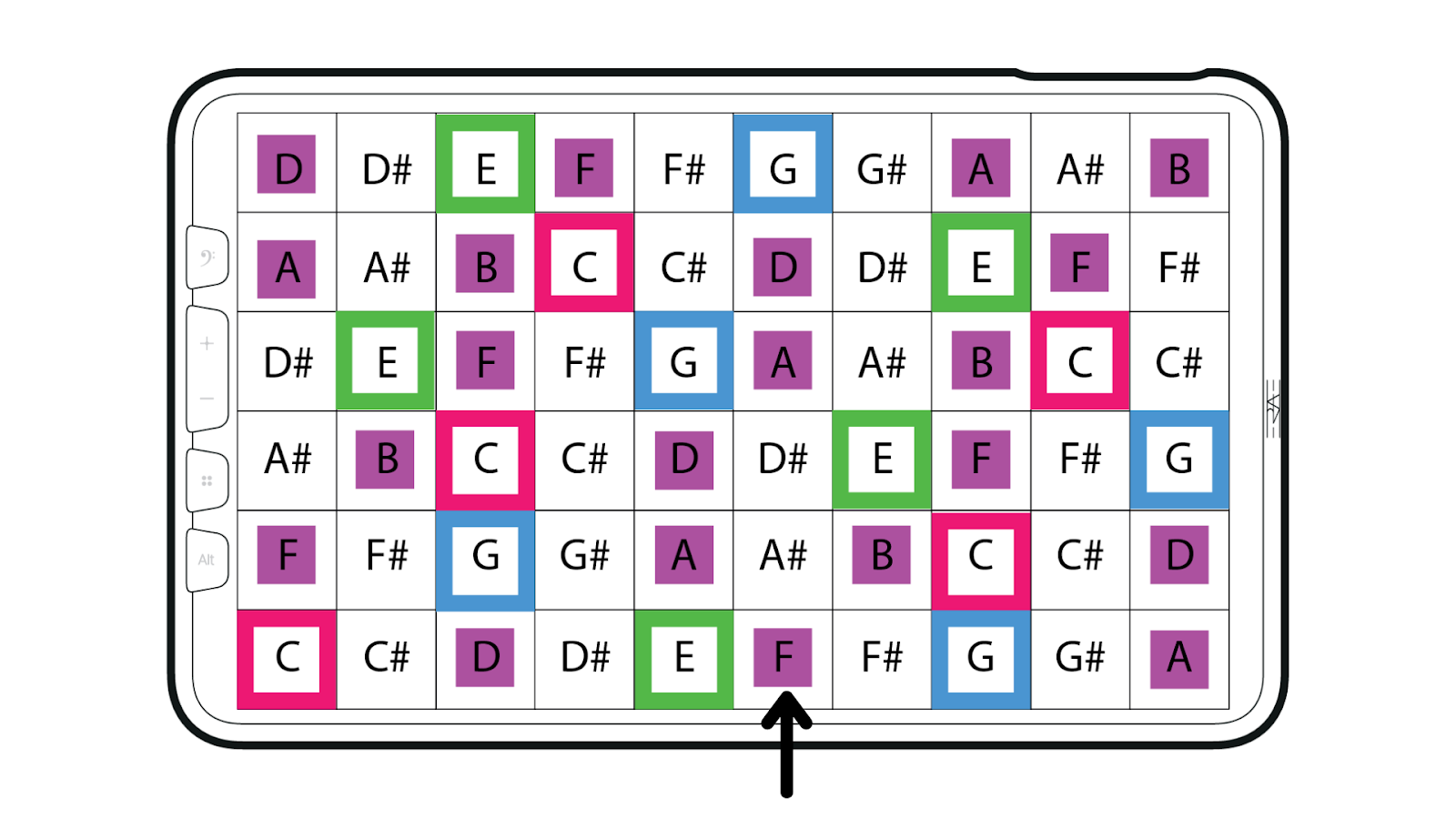
Keygrid representation of C Major scale (first root note C) - Chromatic Mode (off-scale notes are shown)
Keygrid representation of C Major scale (first root note C) - Non-Chromatic Mode (only in-scale notes are shown)
An isomorphic keyboard, has all the notes in the same shape, no black or white keys like the piano setup, every note has the same exact dimension (usually a square). In another article, we delve deep into Why Are Isomorphic Key Grids Useful?
Chromatic mode vs. Scale mode
On our Youtube channel, we explore a in-depth walkthrough to help you get accustomed to the ERAE Touch, here is the video about Scale Selection that shows Chromatic and Scale mode:
Chromatic mode
On the keygrid in chromatic mode, the highlighted keys are the in-scale notes from the scale that you choose.
The big colored squares correspond to the triad of the main chord of the selected scale: the root note, the third and the fifth. The little colored squares correspond to the other notes of the scale (2nd, 4th, 6th and 7th). The white little squares represent the off scale notes.
In this mode all the notes remain in place starting from the root note, the only thing that you see change when changing the scale is the highlighted keys corresponding to the notes in that same scale. That mode allows you to access the off-scale notes between the highlighted keys as well.
For example,
Keygrid representation of C Major scale (first root note C) - Chromatic Mode (off-scale notes are shown)
Scale mode (Non chromatic mode)
On the keygrid in non-chromatic mode, you can only access the notes of the scale you choose. This mode prevents you from triggering any off scale notes and allows you to quickly explore a specific scale without prior knowledge.
In this mode you’ll see only the colored keys: The big colored squares correspond to the triad of the main chord of the selected scale : the root note, the third and the fifth. The little colored squares correspond to the other notes of the scale (2nd, 4th, 6th and 7th).
For example,
Keygrid representation of C Major scale (first root note C) - Non-Chromatic Mode (only in-scale notes are shown)

Keygrid representation of F Harmonic Minor scale (first root note C) - Non-Chromatic Mode (only in-scale notes are shown)
Line Offset
Line offset is the shifted displacement of all notes between the rows in an isomorphic key grid.

A line offset can be used in two different ways. When you have chromatic mode enabled the Line Offset depends on semi-tones. By default, it is of 5 semi-tones.
In non-chromatic mode it depends on degrees not semi-tones, having by default 3 degrees.
You can change the line offset of your keygrid on the ERAE Lab in degrees or semi-tones. The benefit of having full control over your line offset allows you to shape your chords the way you want, on the grid.